Fungal nail infections are a serious medical and social problem.
The pathogen is stable in the external environment and is easily transmitted from person to person.
If you detect the disease in time, you can protect yourself, family members and others from infection.

And to understand when consultation with a qualified doctor is necessary, it does not hurt to know what nail fungus looks like.
There are many types of mushrooms.

And many of them can cause nail diseases.
The general name of this unpleasant sore is onychomycosis.
Depending on which particular fungus led to the development of onychomycosis, the disease is called.
What nail fungus looks like: types of diseases
The most common are:
- Athlete's foot.
- Rubrofitia.
- Trichophytosis.
- Favus.
- Candidiasis.
The causative agents of each of these diseases affect not only the nails, but also the skin and hair.
Therefore, if there are changes in the body, even small at first glance, it is better to go to the doctor.
Perhaps this will help identify the beginning of the disease and stop the spread of the infection.
Athlete's foot
Interestingly, when the disease occurs in the nails, the first and fifth fingers are most often affected.
Why fungi choose them is not known.
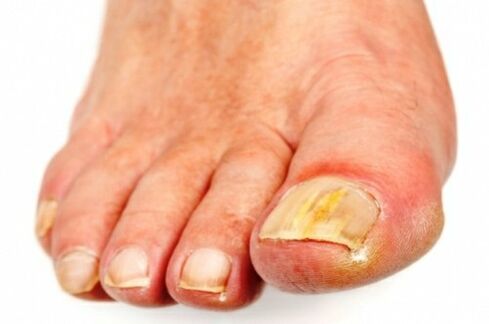
First of all, the appearance of the nails changes:
- Pink gives way to yellow.
- The surface becomes dull and loses its healthy shine.
- Thickening and tubercles appear on the plate.
- Underneath, dense growths (hyperkeratosis) develop.
- Canary-colored spots or lines appear in the thickness of the nail.
The shape of the nail itself lasts quite a long time - several weeks or even months.
The free edge is gradually destroyed.
It becomes as if corroded, uneven.
Another feature of athlete's foot is that the disease only develops in the foot.
The same appearance as the toenail fungus that appears on the hands will not be the same.
If so, it's not athlete's foot.
Rubrofitia
In this case, onychomycosis is caused by a fungus called trichophyton red.
There are three forms of the disease:
- Normotrophic form.
- Hypertrophic.
- Atrophic variety.
In the normotrophic form of onychomycosis, the nail plate does not collapse for a long time.
White or yellow lines (leukonychia) appear in its thickness.
At first they are separated from each other, but gradually they merge into a single point.
In the typical course of the disease, the border at the base of the nail remains unchanged.
Hypertrophic rubrophytosis of nails proceeds differently.
The record initially becomes dull and loses its luster.
It thickens due to growths (hyperkeratosis) underneath.
The nail takes a beak-like shape and crumbles easily.
And this applies not only to the free edge.
The long course of the disease gives the nails a resemblance to bird claws - onychogryphosis.
The atrophic form is also special.
The nail becomes dull and takes on a dirty gray color.
In a fairly short time, the nail plate becomes thinner and destroyed.
Along the edges, at the fold of the nail, the nail tissue remains, but it can also disappear.
Trichophytosis
This fungus causes diseases of the entire surface of the skin.
Onychomycosis develops in only half of patients and affects the fingernails.
What the initial stage of nail fungus with trichophytosis looks like does not allow to make an accurate diagnosis, as it has similarities with other mycoses.
The surface of the nail plate becomes dull and the color becomes gray.
Over time, the nail develops brittleness and crumbles.
In some cases, she may even be removed from her bed.
The process is long and can take several years.
Favus

A synonym of this pathology is scabies.
Children rarely get sick.
The disease has a long and chronic course.
The causative agents are some fungi from the genus Trichophyton.
First, due to subungual keratosis, the plate thickens and moves away from the nail bed.
At the same time, it begins to crumble.
A single yellow spot - scutula - can be observed in its thickness.
It gradually acquires a dirty color.
The death of the nail occurs after a few months from the onset of the disease.
The process is usually accompanied by other hair and skin manifestations.
Candidiasis
Yeast fungi, the causative agent of this infection, usually live in the human body and mucous membranes.
The activation of the infection leads to the appearance of systemic lesions, which can also spread to the nails.
There may be reasons for this
- I. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
- II. Conditions of lack of immunity.
- III.Taking hormonal medications.
- IV.Treatment with cytostatics.
- V. Hypovitaminosis.
Hands and feet are touched with equal frequency.
Visually, how the toenail fungus looks in the initial stage with a yeast infection is difficult to confuse with other diseases.
The nail plate takes on a brown color and becomes bumpy due to lines and depressions.
White spots appear on its surface and thickness.
They are loose and can be easily removed from the nails (if they are superficial).
The nail itself delaminates, being removed from the nail bed.
Along its edges, in the cuticle area, layers of cheese also appear.
It becomes red and inflamed.
Interdigital spaces are also affected.